Source: The Wall Street Journal
Correcting misconceptions about markets, economics, asset prices, derivatives, equities, debt and finance
Saturday, July 30, 2016
Slowest US Post Recession Economic Expansion (GDP Growth) Since 1949: Chart
Posted By Milton Recht
From The Wall Street Journal, "U.S. GDP Grew a Disappointing 1.2% in Second Quarter: Economic growth was well below expectations; cautious business investment offset robust consumer spending" by Eric Morath and Jeffrey Sparshott:
Continuing Decline In Business Investment Is Causing Slow Growth In Productivity, Wages And Jobs
Posted By Milton Recht
From The Wall Street Journal, Opinion, "Make America Grow Again: The economy is stuck on 1% growth as business investment stalls:"
The [2016] second quarter suffered in particular from the same malaise that has marked nearly the entire Obama era—poor business investment. Consumer spending rose smartly at 4.2% in the second quarter, but business investment fell at a 2.2% pace, and companies ran down inventories for the fifth consecutive quarter.
Source: The Wall Street Journal
The nearby chart shows the quarterly contribution to GDP from private “nonresidential fixed investment” since 2013. Business spending on the likes of new factories, equipment and software has subtracted from growth for three straight quarters. Apart from a stretch in 2014, the last three years have been historically weak.
This matters because business investment spurs the growth and productivity gains that produce more jobs and higher wages. As resilient as consumers have been, they can’t drive growth by themselves.
Friday, July 29, 2016
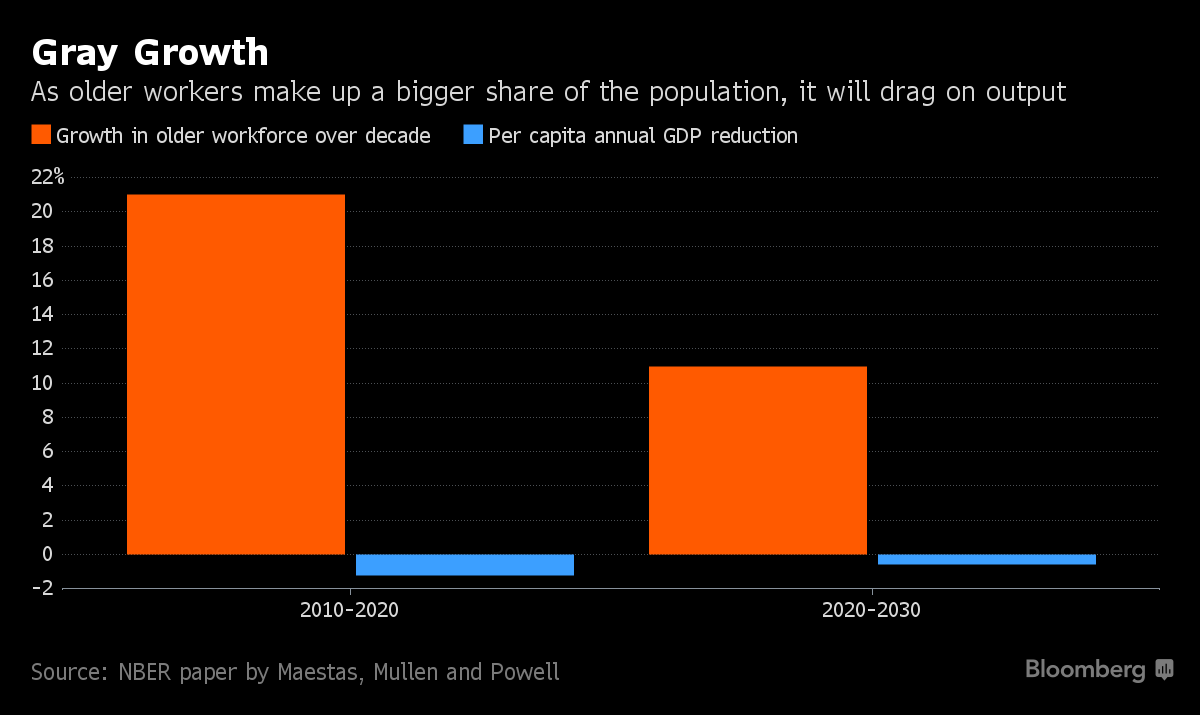
Slowing Labor Force And Productivity Growth From Retiring Baby Boomers Will Lower GDP Growth By 1.2 Percent
Posted By Milton Recht
From BloombergMarkets, "Here's a Reason Baby Boomers Will Curb U.S. Growth this Decade: Output per capita will take a hit as workers older than 60 make up more of the labor force" by Jeanna Smialek:
The retirement of baby-boomers in the decade between 2010 and 2020 will lower GDP growth per capita by 1.2 percentage point a year from what would have been the case if the nation's demographics had held steady, according to a National Bureau of Economic Research study out this week. The bright side is that the dent is only half as deep between 2020 and 2030 as the pace of aging slows.The Social Science Research Network link and abstract of the research study paper follows:
The study is based on a simple idea: population aging is already long underway and has been playing out with varying degrees of intensity across different regions of the country. By looking at variations in state population aging, authors Nicole Maestas at Harvard Medical School, and Kathleen Mullen and David Powell at policy research group RAND Corporation, are able to estimate how a graying workforce affects output, participation rates and productivity.
Source: BloombergMarkets
"The Effect of Population Aging on Economic Growth, the Labor Force and Productivity" by Nicole Maestas, Harvard Medical School - Department of Health Care Policy, Kathleen Mullen, RAND Corporation and David Powell, RAND Corporation, July 2016, NBER Working Paper No. w22452:
Abstract:
Population aging is widely assumed to have detrimental effects on economic growth yet there is little empirical evidence about the magnitude of its effects. This paper starts from the observation that many U.S. states have already experienced substantial growth in the size of their older population and much of this growth was predetermined by historical trends in fertility. We use predicted variation in the rate of population aging across U.S. states over the period 1980-2010 to estimate the economic impact of aging on state output per capita. We find that a 10% increase in the fraction of the population ages 60+ decreases the growth rate of GDP per capita by 5.5%. Two-thirds of the reduction is due to slower growth in the labor productivity of workers across the age distribution, while one-third arises from slower labor force growth. Our results imply annual GDP growth will slow by 1.2 percentage points this decade and 0.6 percentage points next decade due to population aging.
Tuesday, July 26, 2016
20-Year Annualized Average Public Pension Returns At Lowest Level: Funding Shortfall Expected
Posted By Milton Recht
From The Wall Street Journal, "Pension Returns Slump, Squeezing States and Cities: Long-term returns for U.S. public pensions are expected to drop to the lowest levels ever recorded" by Timothy W Martin:
Long-term returns for U.S. public pensions are expected to drop to the lowest levels ever recorded, portending deeper pain for states and cities as a $1 trillion funding gap widens.
Twenty-year annualized returns for public pensions in the U.S. are poised to decline to 7.47% once fiscal 2016 results are released in coming weeks, according to an estimate from Wilshire Trust Universe Comparison Service, which tracks pension investment returns.
***
Source: The Wall Street Journal *** Funding shortcomings often mean taxpayers or workers are asked to chip in more to account for rising liabilities. Every one-percentage-point drop in investment returns represents an increase of 12% in liabilities, according to the Center for Retirement Research at Boston College.
Saturday, July 23, 2016
US Consumer Financial Bureau Restrictions On Payday Lending Will Increase Borrowers' Bankruptcies And Borrowing Costs
Posted By Milton Recht
From The New York Times, DealB%k, "Payday Loan Limits May Cut Abuse but Leave Some Borrowers Looking" by Stacy Cowley:
"We’re very concerned that if this [Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) rule ending payday debt] goes through ...," said Pat Crowley, a spokesman for the Ohio Consumer Lenders Association. "There will be less credit available, and those who find a resource will pay more."
Many economists fear that he is correct — and that low-income consumers will be the ones who are hurt.
In 2004, Georgia made most short-term, high-interest loans illegal. In the wake of that law, Georgia residents paid more bounced-check overdraft fees and became more likely to file for bankruptcy, according to a report by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
A sweeping study of bans on payday lending, scheduled to be published soon in The Journal of Law and Economics, found similar patterns in other states.
Friday, July 22, 2016
52 Percent Of Workers With Access Participate In Employer Health Plans: Private Industry Workers Pay 21 Percent Of Single Coverage Medical Premiums On Average, While Government Workers Pay 13 Percent On Average
Posted By Milton Recht
From The Bureau of Labor Statistics, Economic News Release, Friday, July 22, 2016, USDL-16-1493, "Employee Benefits in the United States:"
The participation rate for employer-sponsored medical care benefits for civilian workers was 52 percent in March 2016, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. The participation rate was 49 percent for private industry workers and 73 percent for state and local government workers. (See tables A and 2, and chart 1.)
The participation rate for employer-sponsored retirement benefits, which include defined benefit and defined contribution plans, was 54 percent for civilian workers. The participation rate was 49 percent for private industry workers and 81 percent for state and local government workers. Differences in retirement plan participation are influenced by the type of plan offered. (See tables A and 1, chart 1, and the technical note.)*** The share of single coverage medical care premiums paid by employees averaged 19 percent for civilian workers, 21 percent for private industry workers, and 13 percent for state and local government workers. (See table 3 and chart 2.) [Emphasis added.]
Employee Benefits in the United States – March 2016 on Scribd
Tuesday, July 19, 2016
My Comment To WSJ "Markets Run Into Skepticism—and Regulators"
Posted By Milton Recht
My comment to The Wall Street Journal, "Markets Run Into Skepticism—and Regulators: Faith in economic freedom used to be a given in the West. Now a misguided trust in government control is growing." by Daniel Yergin:
Markets never cease working.
Government involvement, laws, regulations, subsidies and price control increase the costs of goods and transactions unevenly, which causes markets to cease pricing accurately and to cease allocating capital based on return and risk. If government becomes too heavy handed, illegal markets develop.
Government frequently attempts to do away with buyer's or investor's risk, such as FDIC deposit insurance, Too Big To Fail, Ginnie Mae, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac's direct or implicit backstop government guarantees.
When government hides risk there is too much investment in too risky assets that can lead to severe negative macroeconomic events, such as the housing bubble, its collapse and the recent recession.
Markets need only a rule of law that protects property rights and enforces contracts. More government involvement creates price and risk distortions, which eventually lead to bad investments, bubbles, recessions and slow growth.
Monday, July 18, 2016
CBO Infographic Of US Long-Term Budget Outlook
Posted By Milton Recht
From the Congressional Budget Office, July 15, 2016, "The 2016 Long-Term Budget Outlook: An Infographic:"
This infographic provides an overview of CBO's report, The 2016 Long-Term Budget Outlook. Gain quick insight into why CBO projects a substantial imbalance in the federal budget beyond the next 10 years.
Thursday, July 14, 2016
Women's Lower Math Confidence, Not Lower Math Ability, Causing Women To Switch Out Of STEM Degrees At Higher Rate Than Men
Posted By Milton Recht
From "Calculus factors women out of STEM degrees, researchers find" on ScienceBlog.
Both men and women experience a loss of confidence in their math skills at a similar rate in Calc I, says co-author Jess Ellis, an assistant professor of mathematics in the College of Natural Sciences. The problem, says co-author Bailey Fosdick, an assistant professor of statistics, is that women arrive with lower math confidence to begin with. “When women are leaving, it is because they don’t think they can do it” – not because they can’t do it – she says.*** Students across the country were asked about their interest in and intention to pursue a STEM degree, their test scores, preparation, learning experience, plans and backgrounds – before taking Calculus I and after. A student was considered to “persist” in the STEM track if they went on to take Calculus II.*** Of the students who switched out after Calculus I, when asked why they decided against taking Calculus II, most of the possible explanations fell fairly equally across the genders (too many classes, not needed for major, etc.) – except for one: "I do not believe I understand the ideas of Calculus I well enough to take Calculus II." Of those who had been planning to major in a STEM area, 14 percent of men who switched out listed this as a reason; 35 percent of women did. But fewer than one in five of the departing students of either gender reported that their Calc I grade was actually too low to continue.
Monday, July 11, 2016
Twinkies Hostess Brands Streamlines And Automates: 1,170 Employees And 3 Bakeries Replaced 22,000 Employees And 40 Bakeries
Posted By Milton Recht
From The Washington Post, "What it took to save the Twinkie" by Drew Harwell:
Where the [Hostess Brands, LLC] company just five years ago had 8,000 employees — 75 percent of whom were represented by unions — the company now says in filings that it has a “streamlined employee base” of roughly 1,170 workers. That workforce is the shadow of a once-vast empire, which shortly before its troubles totaled 22,000 workers across more than 40 bakeries.
The company has invested $130 million to upgrade production lines and industrial ovens in its three core bakeries in Indianapolis; Emporia, Kan.; and Columbus, Ga. Its other bakeries have disappeared: The company in 2014 announced it would shutter its long-running bakery in the Chicago suburb of Schiller Park, where the Twinkie was first baked. About 400 jobs were affected.
Based in Kansas City, Mo., the company has closed all 600 or so of its Hostess outlet thrift stores and now delivers directly to warehouses, helping avoid the inefficiencies of regional bakeries, small distribution lines and direct-to-store delivery.
Saturday, July 9, 2016
Over 40 Percent Of US Luxury Home International Buyers Are Chinese
Posted By Milton Recht
From Dow Jones, Mansion Global, "More than 40% of All Foreign Buyers of Luxury Homes in the U.S. Are Chinese: One out of four Chinese buyers in the U.S. purchased $1 million-plus homes" by Fang Block:
Chinese buyers purchased more homes in the U.S. — and at higher prices —than any other international buyers.
In fact, 42% of foreign buyers who purchased homes worth $1 million or more in the U.S. between April 2015 and March 2016 were Chinese, the National Association of Realtors (NAR) reported.
Out of all buyers from mainland China, Taiwan and Hong Kong, about 27% bought homes valued at $1 million and higher, according to an NAR analysis completed for Mansion Global.
By contrast, only 4% of all Canadians — the second-largest group of foreign buyers in the U.S. — bought homes for $1 million or over.
***
Top Four Luxury Markets for Foreign Buyers State Percentage of $1 million-plus homes sold to foreign buyers California 39% Florida 14% New York 14% Washington 6% Source: National Association of Realtors
Tuesday, July 5, 2016
FBI Director James B. Comey's Press Statement on the Investigation of Secretary Hillary Clinton’s Use of a Personal E-Mail System
Posted By Milton Recht
Statement by FBI Director James B. Comey on the Investigation of Secretary Hillary Clinton’s Use of a Personal E-Mail System
Washington, D.C.
July 05, 2016
FBI National Press Office
(202) 324-3691
Remarks prepared for delivery at press briefing.
Good morning. I’m here to give you an update on the FBI’s investigation of Secretary Clinton’s use of a personal e-mail system during her time as Secretary of State.
After a tremendous amount of work over the last year, the FBI is completing its investigation and referring the case to the Department of Justice for a prosecutive decision. What I would like to do today is tell you three things: what we did; what we found; and what we are recommending to the Department of Justice.
This will be an unusual statement in at least a couple ways. First, I am going to include more detail about our process than I ordinarily would, because I think the American people deserve those details in a case of intense public interest. Second, I have not coordinated or reviewed this statement in any way with the Department of Justice or any other part of the government. They do not know what I am about to say.
I want to start by thanking the FBI employees who did remarkable work in this case. Once you have a better sense of how much we have done, you will understand why I am so grateful and proud of their efforts.
So, first, what we have done:
The investigation began as a referral from the Intelligence Community Inspector General in connection with Secretary Clinton’s use of a personal e-mail server during her time as Secretary of State. The referral focused on whether classified information was transmitted on that personal system.
Our investigation looked at whether there is evidence classified information was improperly stored or transmitted on that personal system, in violation of a federal statute making it a felony to mishandle classified information either intentionally or in a grossly negligent way, or a second statute making it a misdemeanor to knowingly remove classified information from appropriate systems or storage facilities.
Consistent with our counterintelligence responsibilities, we have also investigated to determine whether there is evidence of computer intrusion in connection with the personal e-mail server by any foreign power, or other hostile actors.
I have so far used the singular term, “e-mail server,” in describing the referral that began our investigation. It turns out to have been more complicated than that. Secretary Clinton used several different servers and administrators of those servers during her four years at the State Department, and used numerous mobile devices to view and send e-mail on that personal domain. As new servers and equipment were employed, older servers were taken out of service, stored, and decommissioned in various ways. Piecing all of that back together—to gain as full an understanding as possible of the ways in which personal e-mail was used for government work—has been a painstaking undertaking, requiring thousands of hours of effort.
For example, when one of Secretary Clinton’s original personal servers was decommissioned in 2013, the e-mail software was removed. Doing that didn’t remove the e-mail content, but it was like removing the frame from a huge finished jigsaw puzzle and dumping the pieces on the floor. The effect was that millions of e-mail fragments end up unsorted in the server’s unused—or “slack”—space. We searched through all of it to see what was there, and what parts of the puzzle could be put back together.
FBI investigators have also read all of the approximately 30,000 e-mails provided by Secretary Clinton to the State Department in December 2014. Where an e-mail was assessed as possibly containing classified information, the FBI referred the e-mail to any U.S. government agency that was a likely “owner” of information in the e-mail, so that agency could make a determination as to whether the e-mail contained classified information at the time it was sent or received, or whether there was reason to classify the e-mail now, even if its content was not classified at the time it was sent (that is the process sometimes referred to as “up-classifying”).
From the group of 30,000 e-mails returned to the State Department, 110 e-mails in 52 e-mail chains have been determined by the owning agency to contain classified information at the time they were sent or received. Eight of those chains contained information that was Top Secret at the time they were sent; 36 chains contained Secret information at the time; and eight contained Confidential information, which is the lowest level of classification. Separate from those, about 2,000 additional e-mails were “up-classified” to make them Confidential; the information in those had not been classified at the time the e-mails were sent.
The FBI also discovered several thousand work-related e-mails that were not in the group of 30,000 that were returned by Secretary Clinton to State in 2014. We found those additional e-mails in a variety of ways. Some had been deleted over the years and we found traces of them on devices that supported or were connected to the private e-mail domain. Others we found by reviewing the archived government e-mail accounts of people who had been government employees at the same time as Secretary Clinton, including high-ranking officials at other agencies, people with whom a Secretary of State might naturally correspond.
This helped us recover work-related e-mails that were not among the 30,000 produced to State. Still others we recovered from the laborious review of the millions of e-mail fragments dumped into the slack space of the server decommissioned in 2013.
With respect to the thousands of e-mails we found that were not among those produced to State, agencies have concluded that three of those were classified at the time they were sent or received, one at the Secret level and two at the Confidential level. There were no additional Top Secret e-mails found. Finally, none of those we found have since been “up-classified.”
I should add here that we found no evidence that any of the additional work-related e-mails were intentionally deleted in an effort to conceal them. Our assessment is that, like many e-mail users, Secretary Clinton periodically deleted e-mails or e-mails were purged from the system when devices were changed. Because she was not using a government account—or even a commercial account like Gmail—there was no archiving at all of her e-mails, so it is not surprising that we discovered e-mails that were not on Secretary Clinton’s system in 2014, when she produced the 30,000 e-mails to the State Department.
It could also be that some of the additional work-related e-mails we recovered were among those deleted as “personal” by Secretary Clinton’s lawyers when they reviewed and sorted her e-mails for production in 2014.
The lawyers doing the sorting for Secretary Clinton in 2014 did not individually read the content of all of her e-mails, as we did for those available to us; instead, they relied on header information and used search terms to try to find all work-related e-mails among the reportedly more than 60,000 total e-mails remaining on Secretary Clinton’s personal system in 2014. It is highly likely their search terms missed some work-related e-mails, and that we later found them, for example, in the mailboxes of other officials or in the slack space of a server.
It is also likely that there are other work-related e-mails that they did not produce to State and that we did not find elsewhere, and that are now gone because they deleted all e-mails they did not return to State, and the lawyers cleaned their devices in such a way as to preclude complete forensic recovery.
We have conducted interviews and done technical examination to attempt to understand how that sorting was done by her attorneys. Although we do not have complete visibility because we are not able to fully reconstruct the electronic record of that sorting, we believe our investigation has been sufficient to give us reasonable confidence there was no intentional misconduct in connection with that sorting effort.
And, of course, in addition to our technical work, we interviewed many people, from those involved in setting up and maintaining the various iterations of Secretary Clinton’s personal server, to staff members with whom she corresponded on e-mail, to those involved in the e-mail production to State, and finally, Secretary Clinton herself.
Last, we have done extensive work to understand what indications there might be of compromise by hostile actors in connection with the personal e-mail operation.
That’s what we have done. Now let me tell you what we found:
Although we did not find clear evidence that Secretary Clinton or her colleagues intended to violate laws governing the handling of classified information, there is evidence that they were extremely careless in their handling of very sensitive, highly classified information.
For example, seven e-mail chains concern matters that were classified at the Top Secret/Special Access Program level when they were sent and received. These chains involved Secretary Clinton both sending e-mails about those matters and receiving e-mails from others about the same matters. There is evidence to support a conclusion that any reasonable person in Secretary Clinton’s position, or in the position of those government employees with whom she was corresponding about these matters, should have known that an unclassified system was no place for that conversation. In addition to this highly sensitive information, we also found information that was properly classified as Secret by the U.S. Intelligence Community at the time it was discussed on e-mail (that is, excluding the later “up-classified” e-mails).
None of these e-mails should have been on any kind of unclassified system, but their presence is especially concerning because all of these e-mails were housed on unclassified personal servers not even supported by full-time security staff, like those found at Departments and Agencies of the U.S. Government—or even with a commercial service like Gmail.
Separately, it is important to say something about the marking of classified information. Only a very small number of the e-mails containing classified information bore markings indicating the presence of classified information. But even if information is not marked “classified” in an e-mail, participants who know or should know that the subject matter is classified are still obligated to protect it.
While not the focus of our investigation, we also developed evidence that the security culture of the State Department in general, and with respect to use of unclassified e-mail systems in particular, was generally lacking in the kind of care for classified information found elsewhere in the government.
With respect to potential computer intrusion by hostile actors, we did not find direct evidence that Secretary Clinton’s personal e-mail domain, in its various configurations since 2009, was successfully hacked. But, given the nature of the system and of the actors potentially involved, we assess that we would be unlikely to see such direct evidence. We do assess that hostile actors gained access to the private commercial e-mail accounts of people with whom Secretary Clinton was in regular contact from her personal account. We also assess that Secretary Clinton’s use of a personal e-mail domain was both known by a large number of people and readily apparent. She also used her personal e-mail extensively while outside the United States, including sending and receiving work-related e-mails in the territory of sophisticated adversaries. Given that combination of factors, we assess it is possible that hostile actors gained access to Secretary Clinton’s personal e-mail account.
So that’s what we found. Finally, with respect to our recommendation to the Department of Justice:
In our system, the prosecutors make the decisions about whether charges are appropriate based on evidence the FBI has helped collect. Although we don’t normally make public our recommendations to the prosecutors, we frequently make recommendations and engage in productive conversations with prosecutors about what resolution may be appropriate, given the evidence. In this case, given the importance of the matter, I think unusual transparency is in order.
Although there is evidence of potential violations of the statutes regarding the handling of classified information, our judgment is that no reasonable prosecutor would bring such a case. Prosecutors necessarily weigh a number of factors before bringing charges. There are obvious considerations, like the strength of the evidence, especially regarding intent. Responsible decisions also consider the context of a person’s actions, and how similar situations have been handled in the past.
In looking back at our investigations into mishandling or removal of classified information, we cannot find a case that would support bringing criminal charges on these facts. All the cases prosecuted involved some combination of: clearly intentional and willful mishandling of classified information; or vast quantities of materials exposed in such a way as to support an inference of intentional misconduct; or indications of disloyalty to the United States; or efforts to obstruct justice. We do not see those things here.
To be clear, this is not to suggest that in similar circumstances, a person who engaged in this activity would face no consequences. To the contrary, those individuals are often subject to security or administrative sanctions. But that is not what we are deciding now.
As a result, although the Department of Justice makes final decisions on matters like this, we are expressing to Justice our view that no charges are appropriate in this case.
I know there will be intense public debate in the wake of this recommendation, as there was throughout this investigation. What I can assure the American people is that this investigation was done competently, honestly, and independently. No outside influence of any kind was brought to bear.
I know there were many opinions expressed by people who were not part of the investigation—including people in government—but none of that mattered to us. Opinions are irrelevant, and they were all uninformed by insight into our investigation, because we did the investigation the right way. Only facts matter, and the FBI found them here in an entirely apolitical and professional way. I couldn’t be prouder to be part of this organization.
Washington, D.C.
July 05, 2016
FBI National Press Office
(202) 324-3691
Remarks prepared for delivery at press briefing.
Good morning. I’m here to give you an update on the FBI’s investigation of Secretary Clinton’s use of a personal e-mail system during her time as Secretary of State.
After a tremendous amount of work over the last year, the FBI is completing its investigation and referring the case to the Department of Justice for a prosecutive decision. What I would like to do today is tell you three things: what we did; what we found; and what we are recommending to the Department of Justice.
This will be an unusual statement in at least a couple ways. First, I am going to include more detail about our process than I ordinarily would, because I think the American people deserve those details in a case of intense public interest. Second, I have not coordinated or reviewed this statement in any way with the Department of Justice or any other part of the government. They do not know what I am about to say.
I want to start by thanking the FBI employees who did remarkable work in this case. Once you have a better sense of how much we have done, you will understand why I am so grateful and proud of their efforts.
So, first, what we have done:
The investigation began as a referral from the Intelligence Community Inspector General in connection with Secretary Clinton’s use of a personal e-mail server during her time as Secretary of State. The referral focused on whether classified information was transmitted on that personal system.
Our investigation looked at whether there is evidence classified information was improperly stored or transmitted on that personal system, in violation of a federal statute making it a felony to mishandle classified information either intentionally or in a grossly negligent way, or a second statute making it a misdemeanor to knowingly remove classified information from appropriate systems or storage facilities.
Consistent with our counterintelligence responsibilities, we have also investigated to determine whether there is evidence of computer intrusion in connection with the personal e-mail server by any foreign power, or other hostile actors.
I have so far used the singular term, “e-mail server,” in describing the referral that began our investigation. It turns out to have been more complicated than that. Secretary Clinton used several different servers and administrators of those servers during her four years at the State Department, and used numerous mobile devices to view and send e-mail on that personal domain. As new servers and equipment were employed, older servers were taken out of service, stored, and decommissioned in various ways. Piecing all of that back together—to gain as full an understanding as possible of the ways in which personal e-mail was used for government work—has been a painstaking undertaking, requiring thousands of hours of effort.
For example, when one of Secretary Clinton’s original personal servers was decommissioned in 2013, the e-mail software was removed. Doing that didn’t remove the e-mail content, but it was like removing the frame from a huge finished jigsaw puzzle and dumping the pieces on the floor. The effect was that millions of e-mail fragments end up unsorted in the server’s unused—or “slack”—space. We searched through all of it to see what was there, and what parts of the puzzle could be put back together.
FBI investigators have also read all of the approximately 30,000 e-mails provided by Secretary Clinton to the State Department in December 2014. Where an e-mail was assessed as possibly containing classified information, the FBI referred the e-mail to any U.S. government agency that was a likely “owner” of information in the e-mail, so that agency could make a determination as to whether the e-mail contained classified information at the time it was sent or received, or whether there was reason to classify the e-mail now, even if its content was not classified at the time it was sent (that is the process sometimes referred to as “up-classifying”).
From the group of 30,000 e-mails returned to the State Department, 110 e-mails in 52 e-mail chains have been determined by the owning agency to contain classified information at the time they were sent or received. Eight of those chains contained information that was Top Secret at the time they were sent; 36 chains contained Secret information at the time; and eight contained Confidential information, which is the lowest level of classification. Separate from those, about 2,000 additional e-mails were “up-classified” to make them Confidential; the information in those had not been classified at the time the e-mails were sent.
The FBI also discovered several thousand work-related e-mails that were not in the group of 30,000 that were returned by Secretary Clinton to State in 2014. We found those additional e-mails in a variety of ways. Some had been deleted over the years and we found traces of them on devices that supported or were connected to the private e-mail domain. Others we found by reviewing the archived government e-mail accounts of people who had been government employees at the same time as Secretary Clinton, including high-ranking officials at other agencies, people with whom a Secretary of State might naturally correspond.
This helped us recover work-related e-mails that were not among the 30,000 produced to State. Still others we recovered from the laborious review of the millions of e-mail fragments dumped into the slack space of the server decommissioned in 2013.
With respect to the thousands of e-mails we found that were not among those produced to State, agencies have concluded that three of those were classified at the time they were sent or received, one at the Secret level and two at the Confidential level. There were no additional Top Secret e-mails found. Finally, none of those we found have since been “up-classified.”
I should add here that we found no evidence that any of the additional work-related e-mails were intentionally deleted in an effort to conceal them. Our assessment is that, like many e-mail users, Secretary Clinton periodically deleted e-mails or e-mails were purged from the system when devices were changed. Because she was not using a government account—or even a commercial account like Gmail—there was no archiving at all of her e-mails, so it is not surprising that we discovered e-mails that were not on Secretary Clinton’s system in 2014, when she produced the 30,000 e-mails to the State Department.
It could also be that some of the additional work-related e-mails we recovered were among those deleted as “personal” by Secretary Clinton’s lawyers when they reviewed and sorted her e-mails for production in 2014.
The lawyers doing the sorting for Secretary Clinton in 2014 did not individually read the content of all of her e-mails, as we did for those available to us; instead, they relied on header information and used search terms to try to find all work-related e-mails among the reportedly more than 60,000 total e-mails remaining on Secretary Clinton’s personal system in 2014. It is highly likely their search terms missed some work-related e-mails, and that we later found them, for example, in the mailboxes of other officials or in the slack space of a server.
It is also likely that there are other work-related e-mails that they did not produce to State and that we did not find elsewhere, and that are now gone because they deleted all e-mails they did not return to State, and the lawyers cleaned their devices in such a way as to preclude complete forensic recovery.
We have conducted interviews and done technical examination to attempt to understand how that sorting was done by her attorneys. Although we do not have complete visibility because we are not able to fully reconstruct the electronic record of that sorting, we believe our investigation has been sufficient to give us reasonable confidence there was no intentional misconduct in connection with that sorting effort.
And, of course, in addition to our technical work, we interviewed many people, from those involved in setting up and maintaining the various iterations of Secretary Clinton’s personal server, to staff members with whom she corresponded on e-mail, to those involved in the e-mail production to State, and finally, Secretary Clinton herself.
Last, we have done extensive work to understand what indications there might be of compromise by hostile actors in connection with the personal e-mail operation.
That’s what we have done. Now let me tell you what we found:
Although we did not find clear evidence that Secretary Clinton or her colleagues intended to violate laws governing the handling of classified information, there is evidence that they were extremely careless in their handling of very sensitive, highly classified information.
For example, seven e-mail chains concern matters that were classified at the Top Secret/Special Access Program level when they were sent and received. These chains involved Secretary Clinton both sending e-mails about those matters and receiving e-mails from others about the same matters. There is evidence to support a conclusion that any reasonable person in Secretary Clinton’s position, or in the position of those government employees with whom she was corresponding about these matters, should have known that an unclassified system was no place for that conversation. In addition to this highly sensitive information, we also found information that was properly classified as Secret by the U.S. Intelligence Community at the time it was discussed on e-mail (that is, excluding the later “up-classified” e-mails).
None of these e-mails should have been on any kind of unclassified system, but their presence is especially concerning because all of these e-mails were housed on unclassified personal servers not even supported by full-time security staff, like those found at Departments and Agencies of the U.S. Government—or even with a commercial service like Gmail.
Separately, it is important to say something about the marking of classified information. Only a very small number of the e-mails containing classified information bore markings indicating the presence of classified information. But even if information is not marked “classified” in an e-mail, participants who know or should know that the subject matter is classified are still obligated to protect it.
While not the focus of our investigation, we also developed evidence that the security culture of the State Department in general, and with respect to use of unclassified e-mail systems in particular, was generally lacking in the kind of care for classified information found elsewhere in the government.
With respect to potential computer intrusion by hostile actors, we did not find direct evidence that Secretary Clinton’s personal e-mail domain, in its various configurations since 2009, was successfully hacked. But, given the nature of the system and of the actors potentially involved, we assess that we would be unlikely to see such direct evidence. We do assess that hostile actors gained access to the private commercial e-mail accounts of people with whom Secretary Clinton was in regular contact from her personal account. We also assess that Secretary Clinton’s use of a personal e-mail domain was both known by a large number of people and readily apparent. She also used her personal e-mail extensively while outside the United States, including sending and receiving work-related e-mails in the territory of sophisticated adversaries. Given that combination of factors, we assess it is possible that hostile actors gained access to Secretary Clinton’s personal e-mail account.
So that’s what we found. Finally, with respect to our recommendation to the Department of Justice:
In our system, the prosecutors make the decisions about whether charges are appropriate based on evidence the FBI has helped collect. Although we don’t normally make public our recommendations to the prosecutors, we frequently make recommendations and engage in productive conversations with prosecutors about what resolution may be appropriate, given the evidence. In this case, given the importance of the matter, I think unusual transparency is in order.
Although there is evidence of potential violations of the statutes regarding the handling of classified information, our judgment is that no reasonable prosecutor would bring such a case. Prosecutors necessarily weigh a number of factors before bringing charges. There are obvious considerations, like the strength of the evidence, especially regarding intent. Responsible decisions also consider the context of a person’s actions, and how similar situations have been handled in the past.
In looking back at our investigations into mishandling or removal of classified information, we cannot find a case that would support bringing criminal charges on these facts. All the cases prosecuted involved some combination of: clearly intentional and willful mishandling of classified information; or vast quantities of materials exposed in such a way as to support an inference of intentional misconduct; or indications of disloyalty to the United States; or efforts to obstruct justice. We do not see those things here.
To be clear, this is not to suggest that in similar circumstances, a person who engaged in this activity would face no consequences. To the contrary, those individuals are often subject to security or administrative sanctions. But that is not what we are deciding now.
As a result, although the Department of Justice makes final decisions on matters like this, we are expressing to Justice our view that no charges are appropriate in this case.
I know there will be intense public debate in the wake of this recommendation, as there was throughout this investigation. What I can assure the American people is that this investigation was done competently, honestly, and independently. No outside influence of any kind was brought to bear.
I know there were many opinions expressed by people who were not part of the investigation—including people in government—but none of that mattered to us. Opinions are irrelevant, and they were all uninformed by insight into our investigation, because we did the investigation the right way. Only facts matter, and the FBI found them here in an entirely apolitical and professional way. I couldn’t be prouder to be part of this organization.
Asians Are Highest US Hourly Earners By Sex, Race, And Ethnicity: More Asians Have Bachelor And Advanced Degrees Than Whites, Blacks Or Hispanics
Posted By Milton Recht
From Bloomberg, "Asian Men Win the Hourly Earnings Race in America: White and Asian women are getting paid more, too." by Zara Kessler:
The Pew Research Center's review of Current Population Survey data found that, when looking at full- or part-time workers age 16 and up, median hourly earnings for Asian [Asians include Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islanders and include only non-Hispanic Asians] males were $24 last year, compared with $21 for white men. Median hourly earnings for Asian women were $18, compared with $17 for white women. And in a slight twist on the whole notion of the gender wage gap, white and Asian women outpaced black and Hispanic men, whose median hourly earnings in 2015 were $15 and $14, respectively.Differences in educational attainment is the primary cause of income differences in the US among racial and ethnic groups.
Source: Bloomberg
Educational attainment, of course, plays a role: Those with a four-year college degree earn more than those without, and Asians are comparatively very well educated. Fifty-three percent of Asian adults 25 and older had at least a bachelor’s degree in 2015, vs. 36 percent of whites, 23 percent of blacks, and 15 percent of Hispanics. [This includes all those 25 and older in the U.S. civilian non-institutionalized population, not just workers with positive earnings.] Meanwhile, 21 percent of Asians age 25 and older had an advanced degree, compared with 14 percent of whites.
Monday, July 4, 2016
Governments Are Instituted Among Men, Deriving Their Just Powers From The Consent Of The Governed: The Declaration of Independence
Posted By Milton Recht
From the National Archives, the text of "The Declaration of Independence" and a photo of the actual parchment copy:
The Declaration of Independence: A Transcription
IN CONGRESS, July 4, 1776.
The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen united States of America,
When in the Course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature's God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that they should declare the causes which impel them to the separation.
We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness.--That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed, --That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abolish it, and to institute new Government, laying its foundation on such principles and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their Safety and Happiness. Prudence, indeed, will dictate that Governments long established should not be changed for light and transient causes; and accordingly all experience hath shewn, that mankind are more disposed to suffer, while evils are sufferable, than to right themselves by abolishing the forms to which they are accustomed. But when a long train of abuses and usurpations, pursuing invariably the same Object evinces a design to reduce them under absolute Despotism, it is their right, it is their duty, to throw off such Government, and to provide new Guards for their future security.--Such has been the patient sufferance of these Colonies; and such is now the necessity which constrains them to alter their former Systems of Government. The history of the present King of Great Britain is a history of repeated injuries and usurpations, all having in direct object the establishment of an absolute Tyranny over these States. To prove this, let Facts be submitted to a candid world.
He has refused his Assent to Laws, the most wholesome and necessary for the public good.In every stage of these Oppressions We have Petitioned for Redress in the most humble terms: Our repeated Petitions have been answered only by repeated injury. A Prince whose character is thus marked by every act which may define a Tyrant, is unfit to be the ruler of a free people.
He has forbidden his Governors to pass Laws of immediate and pressing importance, unless suspended in their operation till his Assent should be obtained; and when so suspended, he has utterly neglected to attend to them.
He has refused to pass other Laws for the accommodation of large districts of people, unless those people would relinquish the right of Representation in the Legislature, a right inestimable to them and formidable to tyrants only.
He has called together legislative bodies at places unusual, uncomfortable, and distant from the depository of their public Records, for the sole purpose of fatiguing them into compliance with his measures.
He has dissolved Representative Houses repeatedly, for opposing with manly firmness his invasions on the rights of the people.
He has refused for a long time, after such dissolutions, to cause others to be elected; whereby the Legislative powers, incapable of Annihilation, have returned to the People at large for their exercise; the State remaining in the mean time exposed to all the dangers of invasion from without, and convulsions within.
He has endeavoured to prevent the population of these States; for that purpose obstructing the Laws for Naturalization of Foreigners; refusing to pass others to encourage their migrations hither, and raising the conditions of new Appropriations of Lands.
He has obstructed the Administration of Justice, by refusing his Assent to Laws for establishing Judiciary powers.
He has made Judges dependent on his Will alone, for the tenure of their offices, and the amount and payment of their salaries.
He has erected a multitude of New Offices, and sent hither swarms of Officers to harrass our people, and eat out their substance.
He has kept among us, in times of peace, Standing Armies without the Consent of our legislatures.
He has affected to render the Military independent of and superior to the Civil power.
He has combined with others to subject us to a jurisdiction foreign to our constitution, and unacknowledged by our laws; giving his Assent to their Acts of pretended Legislation:
For Quartering large bodies of armed troops among us:
For protecting them, by a mock Trial, from punishment for any Murders which they should commit on the Inhabitants of these States:
For cutting off our Trade with all parts of the world:
For imposing Taxes on us without our Consent:
For depriving us in many cases, of the benefits of Trial by Jury:
For transporting us beyond Seas to be tried for pretended offences
For abolishing the free System of English Laws in a neighbouring Province, establishing therein an Arbitrary government, and enlarging its Boundaries so as to render it at once an example and fit instrument for introducing the same absolute rule into these Colonies:
For taking away our Charters, abolishing our most valuable Laws, and altering fundamentally the Forms of our Governments:
For suspending our own Legislatures, and declaring themselves invested with power to legislate for us in all cases whatsoever.
He has abdicated Government here, by declaring us out of his Protection and waging War against us.
He has plundered our seas, ravaged our Coasts, burnt our towns, and destroyed the lives of our people.
He is at this time transporting large Armies of foreign Mercenaries to compleat the works of death, desolation and tyranny, already begun with circumstances of Cruelty & perfidy scarcely paralleled in the most barbarous ages, and totally unworthy the Head of a civilized nation.
He has constrained our fellow Citizens taken Captive on the high Seas to bear Arms against their Country, to become the executioners of their friends and Brethren, or to fall themselves by their Hands.
He has excited domestic insurrections amongst us, and has endeavoured to bring on the inhabitants of our frontiers, the merciless Indian Savages, whose known rule of warfare, is an undistinguished destruction of all ages, sexes and conditions.
Nor have We been wanting in attentions to our Brittish brethren. We have warned them from time to time of attempts by their legislature to extend an unwarrantable jurisdiction over us. We have reminded them of the circumstances of our emigration and settlement here. We have appealed to their native justice and magnanimity, and we have conjured them by the ties of our common kindred to disavow these usurpations, which, would inevitably interrupt our connections and correspondence. They too have been deaf to the voice of justice and of consanguinity. We must, therefore, acquiesce in the necessity, which denounces our Separation, and hold them, as we hold the rest of mankind, Enemies in War, in Peace Friends.
We, therefore, the Representatives of the united States of America, in General Congress, Assembled, appealing to the Supreme Judge of the world for the rectitude of our intentions, do, in the Name, and by Authority of the good People of these Colonies, solemnly publish and declare, That these United Colonies are, and of Right ought to be Free and Independent States; that they are Absolved from all Allegiance to the British Crown, and that all political connection between them and the State of Great Britain, is and ought to be totally dissolved; and that as Free and Independent States, they have full Power to levy War, conclude Peace, contract Alliances, establish Commerce, and to do all other Acts and Things which Independent States may of right do. And for the support of this Declaration, with a firm reliance on the protection of divine Providence, we mutually pledge to each other our Lives, our Fortunes and our sacred Honor.
The 56 signatures on the Declaration appear in the positions indicated:
Column 1
Georgia:
Button Gwinnett
Lyman Hall
George Walton
Column 2
North Carolina:
William Hooper
Joseph Hewes
John Penn
South Carolina:
Edward Rutledge
Thomas Heyward, Jr.
Thomas Lynch, Jr.
Arthur Middleton
Column 3
Massachusetts:
John Hancock
Maryland:
Samuel Chase
William Paca
Thomas Stone
Charles Carroll of Carrollton
Virginia:
George Wythe
Richard Henry Lee
Thomas Jefferson
Benjamin Harrison
Thomas Nelson, Jr.
Francis Lightfoot Lee
Carter Braxton
Column 4
Pennsylvania:
Robert Morris
Benjamin Rush
Benjamin Franklin
John Morton
George Clymer
James Smith
George Taylor
James Wilson
George Ross
Delaware:
Caesar Rodney
George Read
Thomas McKean
Column 5
New York:
William Floyd
Philip Livingston
Francis Lewis
Lewis Morris
New Jersey:
Richard Stockton
John Witherspoon
Francis Hopkinson
John Hart
Abraham Clark
Column 6
New Hampshire:
Josiah Bartlett
William Whipple
Massachusetts:
Samuel Adams
John Adams
Robert Treat Paine
Elbridge Gerry
Rhode Island:
Stephen Hopkins
William Ellery
Connecticut:
Roger Sherman
Samuel Huntington
William Williams
Oliver Wolcott
New Hampshire:
Matthew Thornton
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)